The manufacturing of medical devices in the modern world is highly regulated and demands precision, innovation, and strict adherence to quality and safety standards.
Advanced technologies such as automation, robotics, and real-time data analytics have transformed the production process, enabling higher efficiency, accuracy, and traceability.
Companies must comply with stringent global regulations, such as FDA and ISO standards, to ensure product safety and efficacy.
With the growing complexity of medical devices and the need for rapid market delivery, manufacturers are increasingly adopting smart systems that streamline processes, reduce human error, and ensure consistent, high-quality outcomes.
The transition from medical device design to manufacturing presents numerous challenges, including the accurate translation of complex CAD designs into executable processes, seamless BOM imports, and the precise documentation of intricate components such as harnesses, bridges, and their routing. Ensuring that all design elements are correctly captured while maintaining compliance with strict regulatory requirements adds further complexity.
PROMAI’s Gen addresses these challenges by importing CAD designs and BOM and automatically generating structured, detailed executable manufacturing processes and embedding real-time validation checks. This ensures that every manufacturing step aligns perfectly with the original design intent, streamlining production, reducing errors, and ensuring regulatory compliance with minimal manual effort.
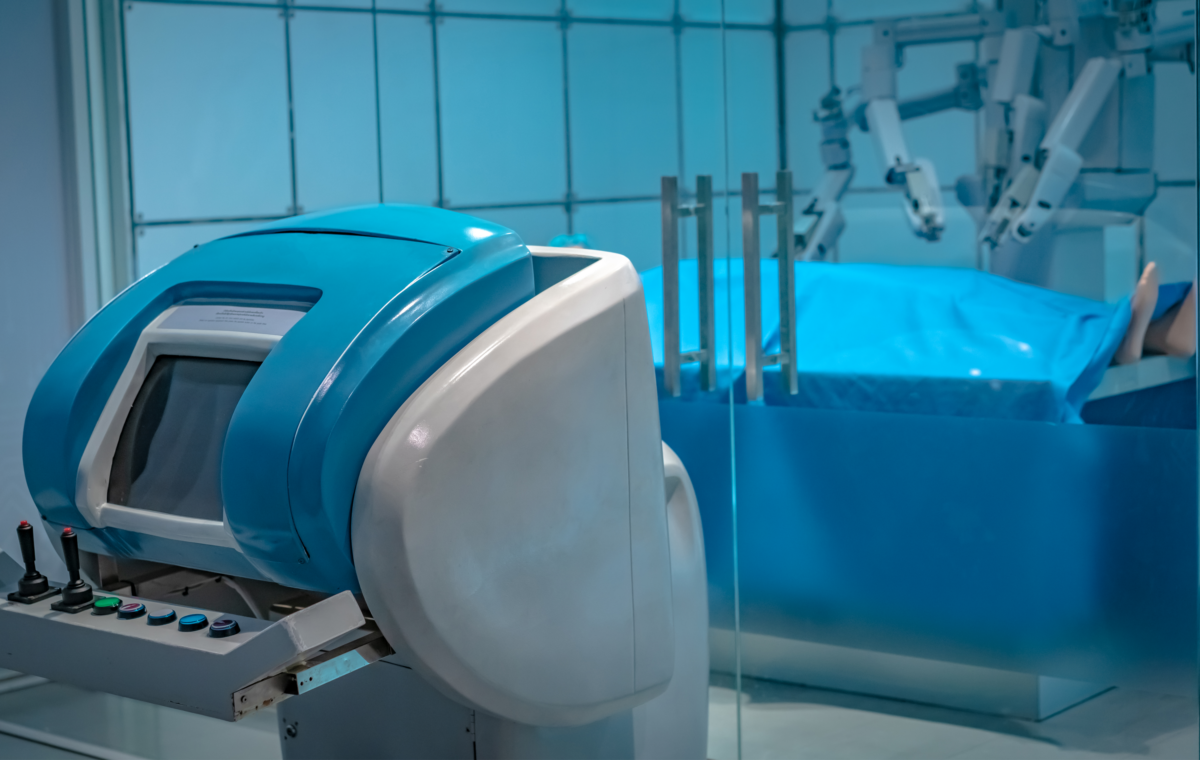

Prototyping medical devices presents significant challenges, including the need for rapid iteration, precision, and error-free execution while ensuring full traceability and compliance. Managing complex machinery like 3D printers and translating designs into production-ready prototypes often involves time-consuming manual processes prone to errors.
PROMAI’s Shield solves these issues by automatically generating machine-ready code for devices such as 3D printers and providing clear, visual step-by-step instructions.
This approach enables rapid, precise prototyping with minimal human error, producing an error free flows, speeding up development, and ensuring that every prototype meets design specifications and regulatory requirements.
Moving from prototyping to full-scale fabrication of medical devices presents significant challenges, including optimizing production line setups, dynamically scheduling tasks to meet key performance indicators (KPIs), ensuring consistent process execution, and minimizing downtime through effective fault isolation and preventive maintenance.
PROMAI’s Suite streamlines this transition by offering optimized production line planning and real-time, dynamic task scheduling to maximize efficiency. The Suite generates verifiable, multilingual step-by-step processes, ensuring clear communication across global teams.
Additionally, its advanced fault isolation and preventive maintenance features help reduce errors and equipment failures, enabling high-quality, consistent, and scalable manufacturing.

Assembly and testing of medical devices are highly intricate processes, requiring strict adherence to design specifications, precision in handling complex components, and rigorous testing to ensure safety and compliance. Challenges arise from managing numerous assembly steps, maintaining traceability, and ensuring consistent quality across production batches.
PROMAI’s Suite resolves these challenges by providing automated, verifiable assembly instructions with clear, step-by-step guidance and real-time validation. Its integrated testing framework embeds measurable checkpoints at each critical stage, ensuring that defects are quickly identified and addressed. This approach guarantees accurate assembly, faster testing cycles, and full compliance with industry standards, significantly improving production efficiency and product reliability.
Testing is a crucial step to ensure the functionality and safety of the medical device. Various types of tests are conducted, including performance testing, stress testing, and functional testing, to verify that the device operates as intended and meets the required performance and safety standards.
PROMAI’sShield utilizes the test and fault isolation procedures generated by PROMAI’s Gen, ensuring the device’s functionality is thoroughly proven and validated.
Quality control procedures are integrated throughout the manufacturing process to maintain high standards in medical device production. This involves thorough inspection, verification, and validation of the device’s components and subsystems to ensure they meet the stringent requirements of the healthcare industry. Quality control measures include visual inspections, electrical and mechanical testing, biocompatibility assessments, and strict adherence to regulatory guidelines such as FDA or ISO standards to ensure safety, reliability, and compliance in medical applications.
Medical robots must comply with strict regulatory requirements, such as those set by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in the United States or similar authorities in other countries. Manufacturers must ensure their robots meet the necessary safety and performance standards, and documentation needs to be prepared for regulatory submission.
Integrating PROMAI’sSuite into the design and manufacturing processes generates complete and validated manufacturing processes “PROMAI’s Gen” and complete test and QA reports of each manufacturing process “PROMAI’s Shield” reduces time to acknowledge the FDA this time to market is reduced dramatically.
Packing and shipping medical devices involve critical challenges, including ensuring proper labeling, maintaining traceability, adhering to strict regulatory requirements, and protecting sensitive devices during transit. Any errors in this process can lead to compliance issues or product damage.
PROMAI’s Suite resolves these challenges by generating precise, step-by-step packing instructions, including automated label generation and verification for compliance. The Suite ensures that every device is packed according to predefined standards and creates a complete digital record for traceability.
Additionally, dynamic scheduling and real-time monitoring help streamline the shipping process, ensuring timely delivery while maintaining product integrity throughout the supply chain.
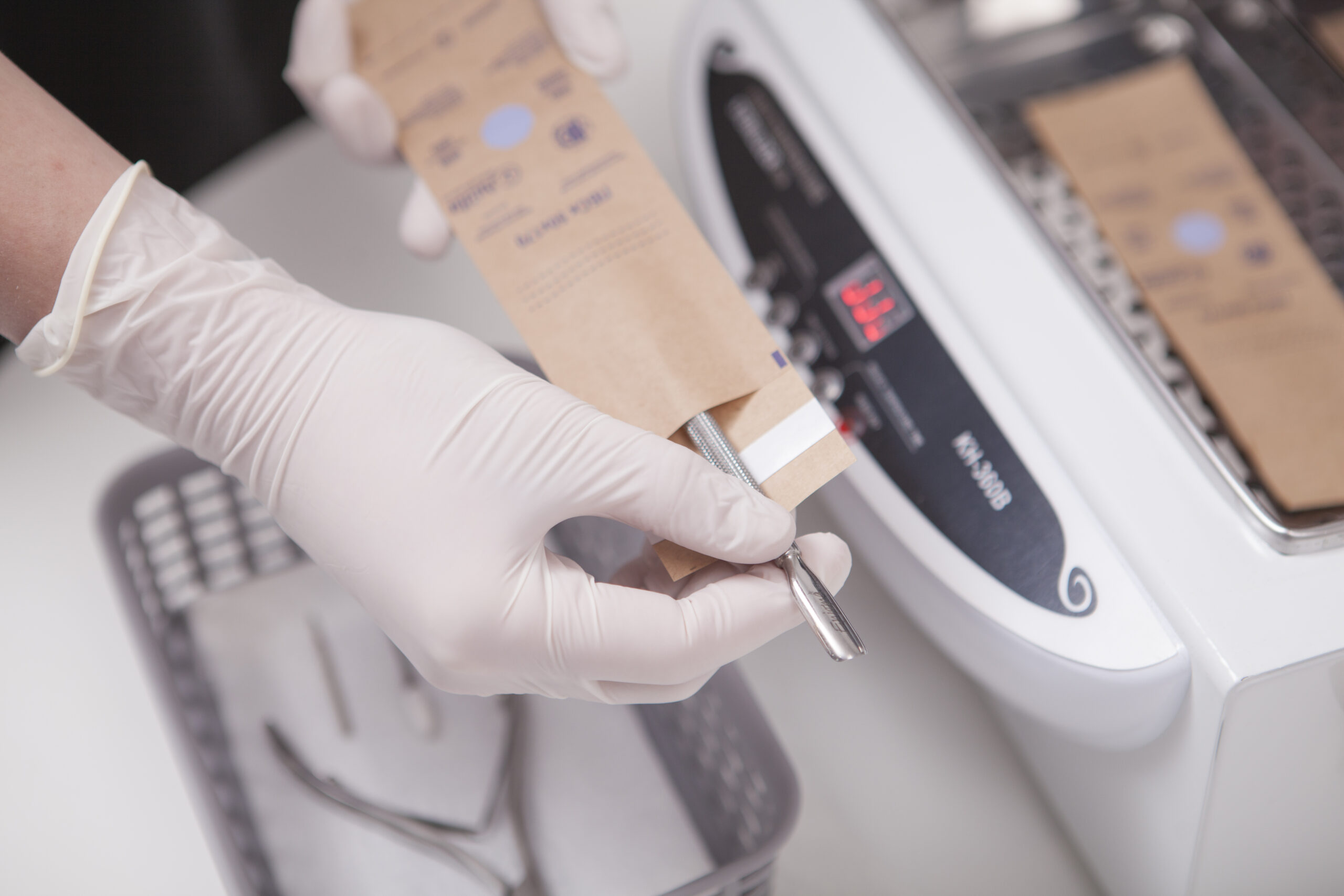


Unpacking, sterilization, calibration, and shipping of medical devices are critical processes that require strict adherence to protocols to ensure device safety, accuracy, and compliance. Errors in these steps can lead to contamination, malfunction, or regulatory non-compliance.
PROMAI’s Suite addresses these challenges by providing detailed, verifiable instructions for each step, from unpacking and sterilization procedures to precise calibration tasks.
The Suite ensures that each process is correctly documented and validated in real time, enabling traceability and compliance with stringent standards. By automating task scheduling and providing real-time monitoring,
PROMAI ensures error-free execution and streamlined shipping, guaranteeing that devices arrive ready for immediate use.

visibility_offDisable flashes
titleMark headings
settingsBackground Color
zoom_outZoom out
zoom_inZoom in
remove_circle_outlineDecrease font
add_circle_outlineIncrease font
spellcheckReadable font
brightness_highBright contrast
brightness_lowDark contrast
format_underlinedUnderline links
font_downloadMark links